Send this article to a friend:
November
01
2023
Send this article to a friend: November |
Supercritical CO2 pilot aims to make steam turbines obsolete
Ribbons were cut at the Supercritical Transformational Electric Power (STEP) pilot plant in Texas on October 27 as it was declared "mechanically complete" by project partners Southwest Research Institute (SwRI), GTI Energy, GE Vernova, and the U.S. Department of Energy. The device in the image above is the world's first supercritical carbon dioxide turbine. Roughly the size of a desk, is a 10-megawatt turbine capable of powering around 10,000 homes. Ten megawatts is pretty small potatoes in the energy business, but to do it with a turbine this tiny? That could prove to be a revolutionary feat. Carbon dioxide goes supercritical when the temperature and pressure are above about 31 °C (88 °F) and 74 bar (1,070 psi), respectively. At this point, it stops acting like a gas or a liquid, and instead starts acting something like a gas with the density of a liquid. Past this point, relatively small changes in temperature can cause significant changes in density. Water can of course go supercritical too – it just takes a lot more energy, requiring a temperature and pressure over 373 °C (703 °F) and 220 bar (3,191 psi).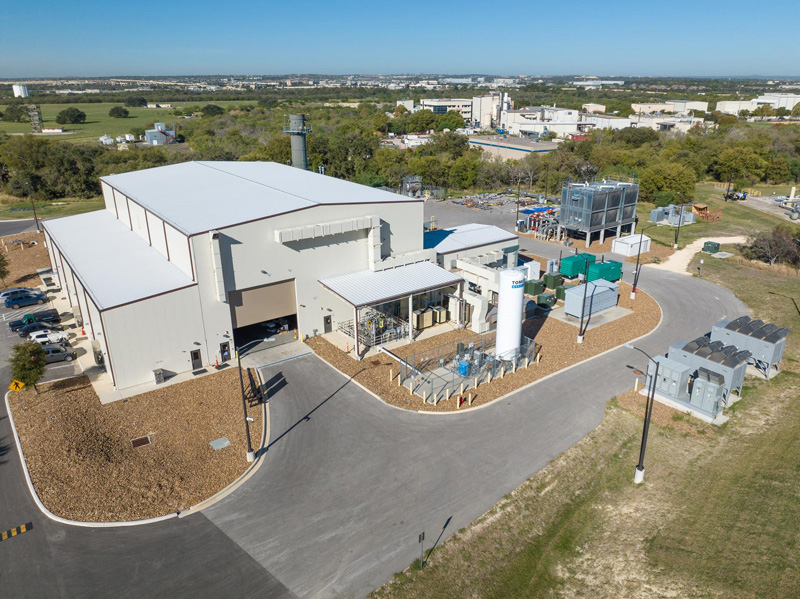  The STEP facility in San Antonio has been declared "mechanically complete" and is due for commissioning in 2024 Southwest Research Institute The properties of this supercritical CO2 fluid make it ideal for energy extraction in a closed-loop system, and back in 2016, General Electric announced it would start building a pilot plantto prove the idea in a commercially relevant installation, expecting to achieve 10 MW at an extraction efficiency of 50% – around 10% better than current steam turbines, which operate in the mid-40s – using a turbine about one-tenth the size. Such a turbine could significantly reduce the capital cost of setting up any power generator reliant on heat and turbines; not only will the smaller turbines be cheaper, but they're so much more compact that you'll need less land for a given power plant. It'd also produce more power from a given heat source, and by default reduce the per-unit carbon emissions even of coal and gas-based generators. And on top of that, it'll be much faster to start up and switch on. Running at around 700 °C (1,292 °F), GE's prototypes take about two minutes to start generating, where steam turbines take at least half an hour. So these CO2 turbines will be much quicker to respond to load demands, making them even more useful in a renewables-based grid. Once proven, the tech could scale up to utility-relevant sizes and start displacing steam turbines in power plants. That includes fossil-fueled plants, as well as certain nuclear, geothermal, concentrated solar, and other installations. There's still work to go before the pilot plant is commissioned, but the consortium expects it'll start operating in 2024.
Source: Southwest Research Institute
|
Send this article to a friend:
 |
 |
 |